RoboCare: Autonomous Medical Automation Assistant
Role: Lead Programmer & Systems Designer
RoboCare is an intelligent, autonomous robotic system designed to modernize hospital logistics. By handling the transport of medicines and biological materials, RoboCare reduces the physical workload on medical staff and significantly minimizes the risk of cross-infection in clinical environments.
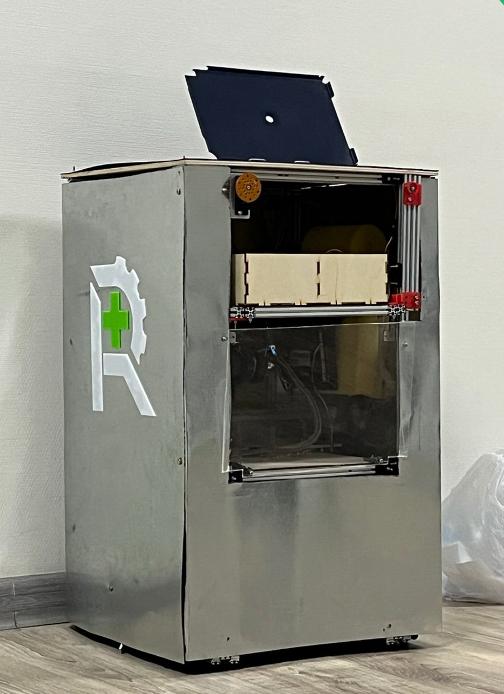

The Problem
Healthcare workers face two critical challenges: burnout from high workloads and high exposure to infectious diseases.
- Infection Risk: In Kazakhstan alone, over 13,000 medical workers were infected with COVID-19, with 182 fatal cases.
- Operational Inefficiency: Nurses and doctors spend valuable time on manual logistics rather than patient care.
- Safety Control: Traditional delivery methods lack secure verification, leading to potential medication errors.
The Solution: Secure, Contactless Delivery
RoboCare is not just a delivery cart; it is a smart assistant that integrates seamlessly into the hospital workflow.
- Autonomous Navigation: The robot navigates hospital corridors independently using a combination of Husky Lens vision and AprilTags (ceiling markers) for precise mapping and obstacle avoidance.
- Secure Dispensing: To ensure the right patient receives the right medication, the robot utilizes Face ID biometric verification. The storage compartment only unlocks when the recipient's face is recognized.
- Self-Sterilization: Equipped with internal UV lamps, the robot automatically disinfects its cargo area between deliveries to maintain hygiene standards.
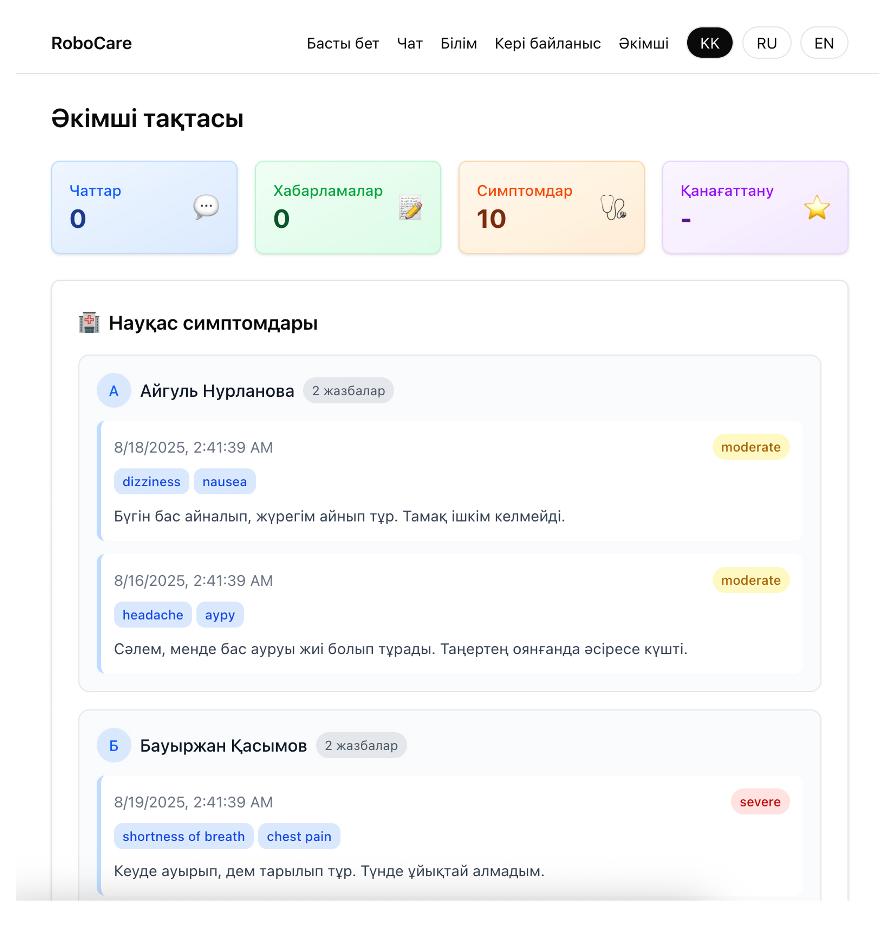
- AI Patient Assistant: Beyond delivery, the system features an AI chatbot interface that can perform preliminary symptom surveys with patients.
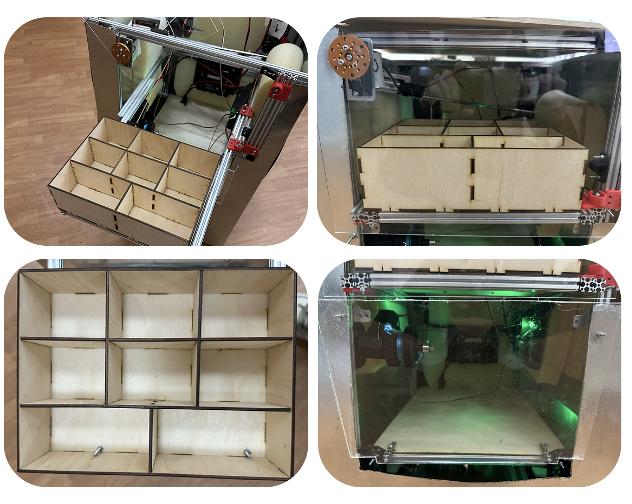

Technology Stack
The system was engineered to be robust yet cost-effective.
- Mobile Platform: Custom chassis with Mecanum wheels for omnidirectional movement in narrow hospital corridors. It features a 5kg payload capacity and 1-2 hours of continuous operation (5.5-hour standby) with auto-docking capabilities.
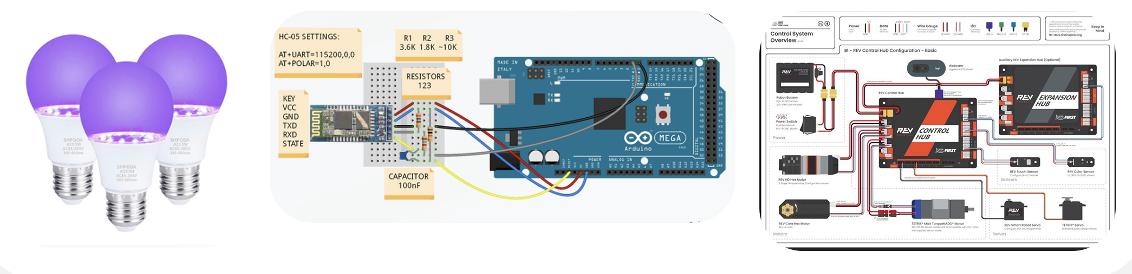
- Control System: Powered by a REV Control Hub and IMU sensors. I coded autonomous navigation using RRT pathing* and sensor fusion systems for stability and precise movement logic.
- Software Integration: I developed an accompanying mobile application for doctors to send delivery tasks and track the robot's route in real-time.
- Hardware: Includes thermal containers for temperature-sensitive drugs and specialized drawers for organized storage.
Real-World Testing & Validation
We followed an iterative "Customer Development" process, testing prototypes in actual medical facilities:
- Dental Clinic: We deployed the first prototype to test loading/unloading ergonomics and gather feedback from administrators.
- City Clinic No. 7: Testing the updated prototype in a busy public clinic helped us refine the navigation algorithms for complex, dynamic environments.
- Mediker Medical Center: The final validation proved the robot's ability to operate safely around patients and confirmed the utility of the thermal container system.
Competitive Advantage
Compared to US-based competitors like TUG or Moxi, RoboCare offers a distinct advantage:
- Cost Efficiency: While competitors cost between 15,000+, RoboCare’s production cost is approximately $1,145.
- Security: Unlike many competitors, RoboCare includes native Face-ID integration for secure access.
- Hygiene: Built-in UV disinfection is a standard feature, not an add-on.
Future Roadmap
The project is moving toward mass scalability and advanced certification.
- Technical Upgrades: Transitioning to LiDAR-based SLAM navigation for even greater autonomy without visual markers.
- Integration: Implementing HL7/FHIR standards to allow the robot to communicate directly with hospital Electronic Health Records (EHR).
- Analytics: Developing a predictive analytics module to forecast clinic supply needs based on historical data.