Derma Diagnostics: Privacy-Preserving Skin Lesion Triage
Role: Independent Researcher
A lightweight, browser-based skin lesion classifier designed for rural clinics. This project implements a MobileNetV1 CNN fine-tuned on the HAM10000 dataset to classify 7 types of skin lesions directly on client devices, ensuring patient privacy and enabling offline usage.
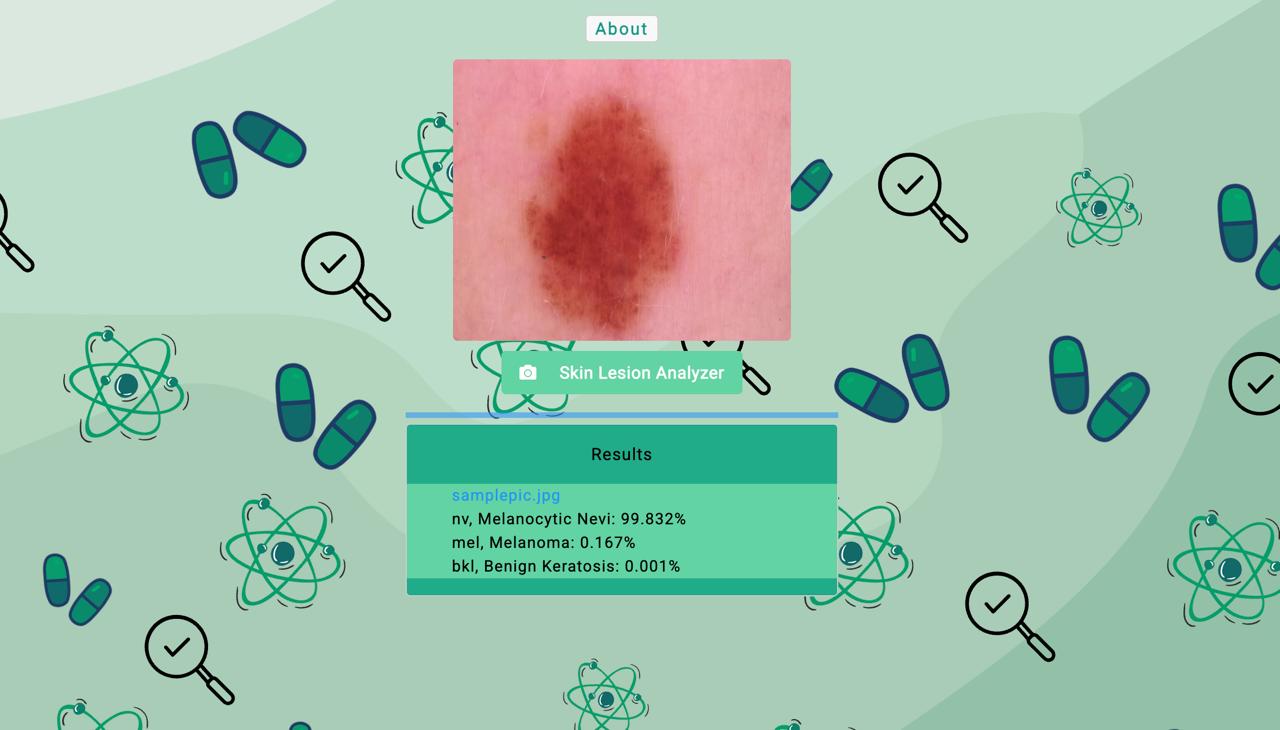 The Derma Diagnostics web interface for skin lesion analysis
The Derma Diagnostics web interface for skin lesion analysis
Abstract
Early melanoma detection saves lives, yet rural clinics often lack dermatologists and reliable connectivity. We present a privacy-preserving, browser-based skin-lesion classifier that returns top-three diagnostic predictions in under 2 seconds on standard smartphones.
Using the HAM10000 dataset with leakage-safe lesion-level splitting, we fine-tuned MobileNetV1 with the final 30 layers trainable. The model achieves ROC-AUC 0.979 for melanoma detection and 96% top-3 accuracy across 7 lesion types. The TensorFlow.js model runs entirely client-side, safeguarding patient privacy while enabling rapid, accurate triage in resource-limited settings.
Key Features
Privacy-Preserving
All inference happens locally in the browser using TensorFlow.js. No patient images are uploaded to a server, ensuring complete data privacy and HIPAA compliance.
Offline Capable
Once loaded, the application works without an internet connection, making it suitable for remote areas with unreliable connectivity.
High Performance
- ROC-AUC 0.979 for melanoma detection
- 96% top-3 accuracy on validation set
- 87% melanoma sensitivity at 95% specificity
- Less than 2s inference time on mobile devices
Leakage-Safe Training
Implements lesion-level stratified splitting to prevent data leakage. Different images of the same lesion never appear in both train and validation sets, ensuring rigorous evaluation.
Technical Implementation
Model Architecture
The system uses MobileNetV1 as the base architecture, fine-tuned specifically for skin lesion classification:
- Base Model: MobileNetV1 (pre-trained on ImageNet)
- Fine-tuning: Final 30 layers trainable
- Dataset: HAM10000 (10,015 dermatoscopic images)
- Classes: 7 types of skin lesions:
- Actinic keratoses and intraepithelial carcinoma (akiec)
- Basal cell carcinoma (bcc)
- Benign keratosis-like lesions (bkl)
- Dermatofibroma (df)
- Melanoma (mel)
- Melanocytic nevi (nv)
- Vascular lesions (vasc)
Data Processing
Leakage-Safe Splitting: The dataset is split at the lesion level, not the image level. This ensures that:
- Multiple images of the same lesion stay in the same split
- No information leakage between training and validation sets
- More realistic evaluation of model performance
Data Augmentation: Applied during training to improve generalization:
- Random rotations (180°)
- Horizontal and vertical flips
- Brightness and contrast adjustments
- Zoom and crop variations
Deployment
TensorFlow.js Conversion: The trained model is converted to TensorFlow.js format, enabling:
- Client-side inference in web browsers
- No server-side processing required
- Cross-platform compatibility (desktop, mobile, tablet)
Performance Optimization:
- Model quantization for faster loading
- Lazy loading of model weights
- Efficient image preprocessing pipeline
Results
The model was evaluated on a held-out validation set of 159 unique lesions (1,039 images) with strict lesion-level splitting:
Binary Melanoma Detection
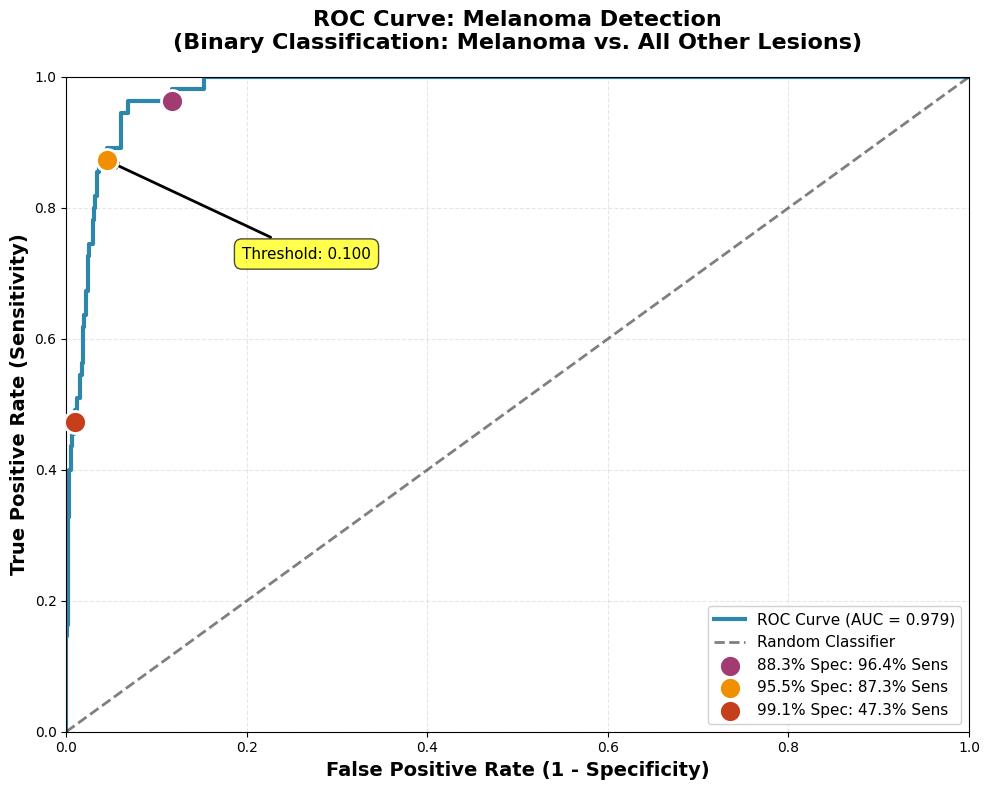 ROC curve for melanoma detection showing AUC of 0.979
ROC curve for melanoma detection showing AUC of 0.979
- ROC-AUC: 0.979
- Sensitivity at 95% Specificity: 87.3%
- Sensitivity at 90% Specificity: 96.4%
- Best F1-Score: 0.691
Multi-Class Performance
- Top-1 Accuracy: 73.3%
- Top-2 Accuracy: 89.0%
- Top-3 Accuracy: 95.8%
- Macro F1-Score: 0.641
Inference Speed
- Desktop (Chrome): ~450ms
- Mobile (Android): ~1.2s
- Mobile (iOS Safari): ~1.5s
Clinical Significance
The ROC-AUC of 0.979 demonstrates strong discriminative ability for melanoma detection. The 87% sensitivity at 95% specificity provides a clinically meaningful tradeoff for triage applications:
- 87% of melanomas correctly flagged for specialist review
- 95% of non-melanomas correctly ruled out
- Top-3 predictions provide clinicians with differential diagnoses
- Fast inference enables real-time decision support
Repository Structure
├── data/ # Dataset storage (excluded from git)
│ ├── processed_grouped/ # Organized train/val folders after lesion-level split
│ └── splits/ # Split metadata (CSVs)
├── src/
│ ├── grouped_split.py # Script for leakage-safe data preparation
│ └── prepare_data.py # Basic data preparation script
├── notebooks/
│ └── ML4H_Training_Notebook.ipynb # Main training and evaluation notebook
├── models/ # Saved model checkpoints
├── figures/ # ROC curves and performance visualizations
└── README.mdGetting Started
Prerequisites
- Python 3.8+
- TensorFlow 2.x
- Node.js (for local serving if needed)
Installation
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Nurbek-web/dermaai.git
cd dermaai- Install Python dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txtData Preparation
- Download the HAM10000 dataset from the Harvard Dataverse or Kaggle
- Place the unzipped files into the
data/directory - Run the grouped split script to prepare the data with leakage prevention:
python src/grouped_split.pyThis will create data/processed_grouped/ with train and val subdirectories.
Training
Open notebooks/ML4H_Training_Notebook.ipynb in Jupyter Notebook or Google Colab to reproduce the training process. The notebook covers:
- Data loading with augmentation
- MobileNetV1 transfer learning
- Class weighting with melanoma importance boost
- Evaluation metrics (ROC-AUC, Sensitivity, Specificity)
- Calibration (Temperature Scaling)
- Conversion to TensorFlow.js format
Impact and Applications
Rural Healthcare
This project addresses critical gaps in rural healthcare:
- Limited Access: Many rural clinics lack dermatologists
- Connectivity Issues: Unreliable internet prevents cloud-based solutions
- Privacy Concerns: Patient data must remain secure and local
- Cost Constraints: Expensive hardware is not feasible
Clinical Workflow Integration
The system is designed for triage, not diagnosis:
- Provides top-3 predictions to guide clinical decision-making
- Fast results enable immediate patient counseling
- Offline capability ensures availability regardless of connectivity
- Privacy-preserving design meets healthcare data protection requirements
Future Development
Potential improvements and extensions:
- External Validation: Testing on independent datasets to assess generalization
- Expanded Dataset: Training on larger, more diverse populations
- Multi-modal Input: Incorporating patient history and clinical metadata
- Mobile App: Native mobile application for better performance
- Telemedicine Integration: API for integration with telemedicine platforms
Technical Stack
- Machine Learning: TensorFlow, MobileNetV1
- Deployment: TensorFlow.js
- Frontend: HTML5, JavaScript
- Data Processing: Python, NumPy, Pandas
- Training: Google Colab, Jupyter Notebooks
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Citation
If you use this code or methodology, please cite:
Taizhanov, Nurbek. "Derma Diagnostics: Privacy-Preserving Skin Lesion
Classification with Edge Inference." (2025, in preparation).Derma Diagnostics represents a practical application of machine learning to address real-world healthcare challenges. By prioritizing privacy, accessibility, and performance, this project demonstrates how AI can be deployed responsibly to improve healthcare outcomes in resource-limited settings.